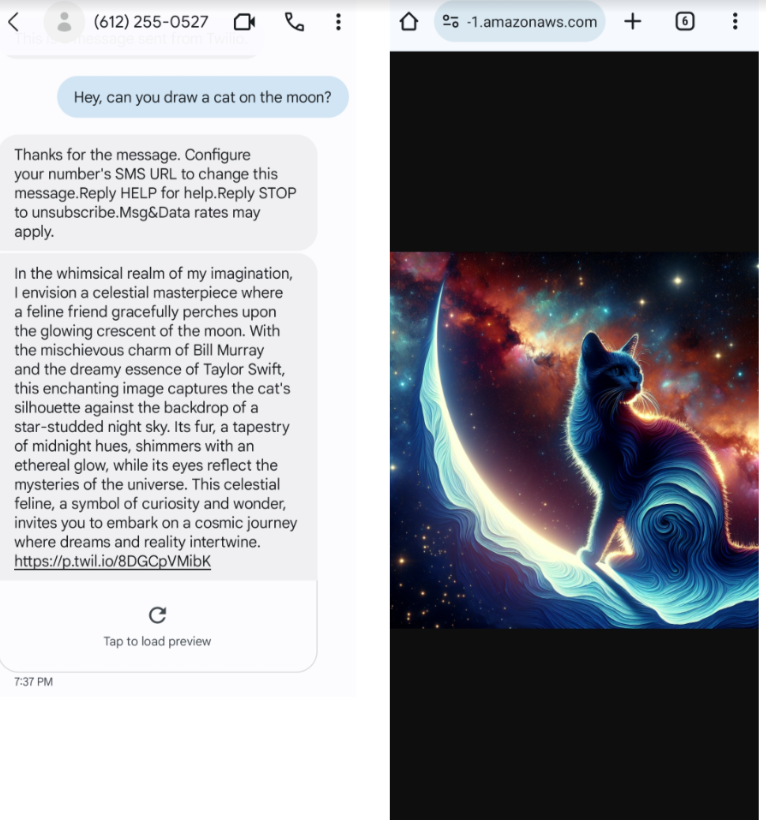
Step 1. Create OpenAI models with a bit of personality
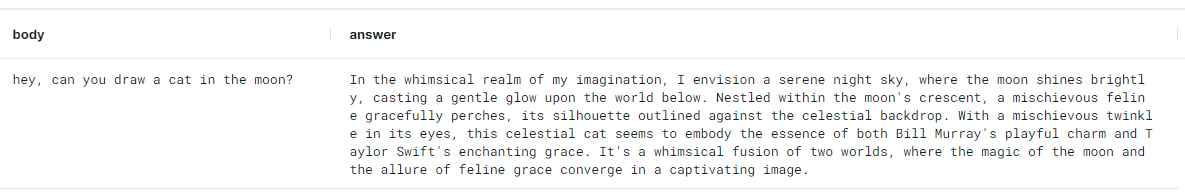
In order to create an AI model, you’ll need an OpenAI account and an API key. You’ll also need a MindsDB installation - you can find an open-source version here. Then go to your MindsDB SQL Editor and enter the following commands to create AI models: 1. Model to generate a text response: Before creating an OpenAI model, please create an engine, providing your OpenAI API key:CREATE MODEL command creates and deploys the model within MindsDB. Here we use the OpenAI GPT-3.5 Turbo model to generate text responses to users’ questions. The prompt_template message sets the personality of the bot - here, it is a mashup of Bill Murray and Taylor Swift.
Please note that the prompt_template message contains the {{body}} variable, which will be replaced by the body of the received message upon joining the model with the table that stores messages.
Let’s test it:
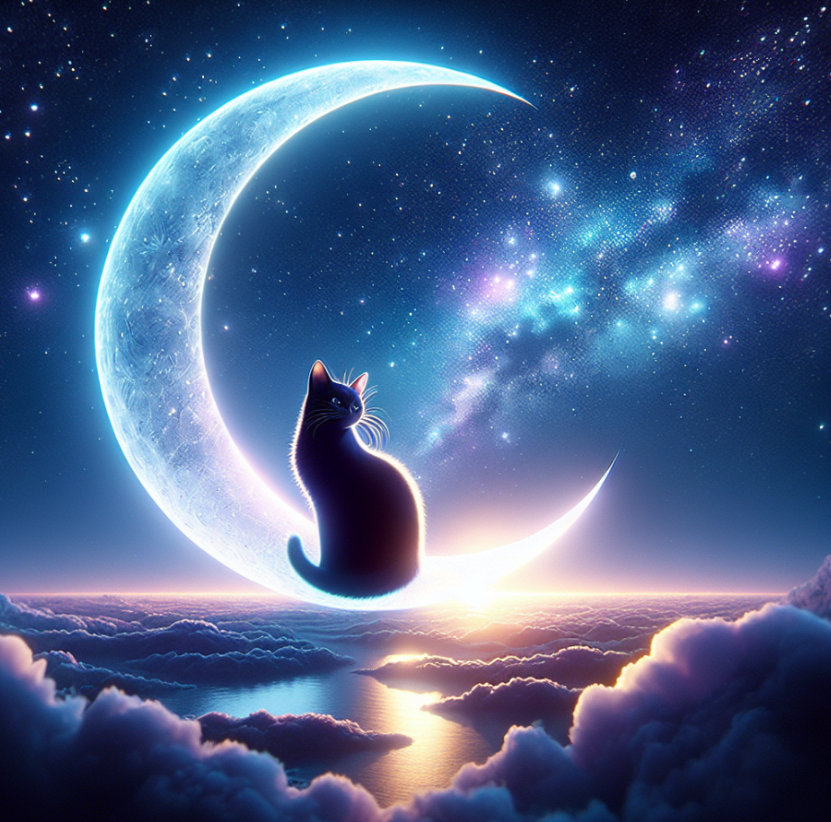
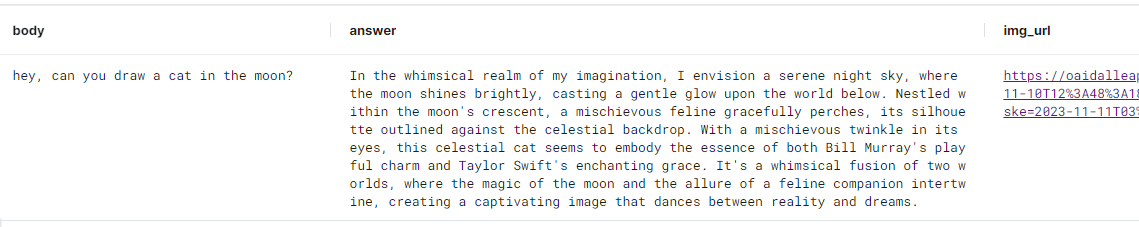
CREATE MODEL command creates and deploys the model within MindsDB. Here we use the OpenAI DallE 3 model to generate images based on the Billor Swift’s text response. The prompt_template message contains the {{answer}} variable. This variable is replaced by the prediction of the previous model upon chaining the two models.
Let’s test it:

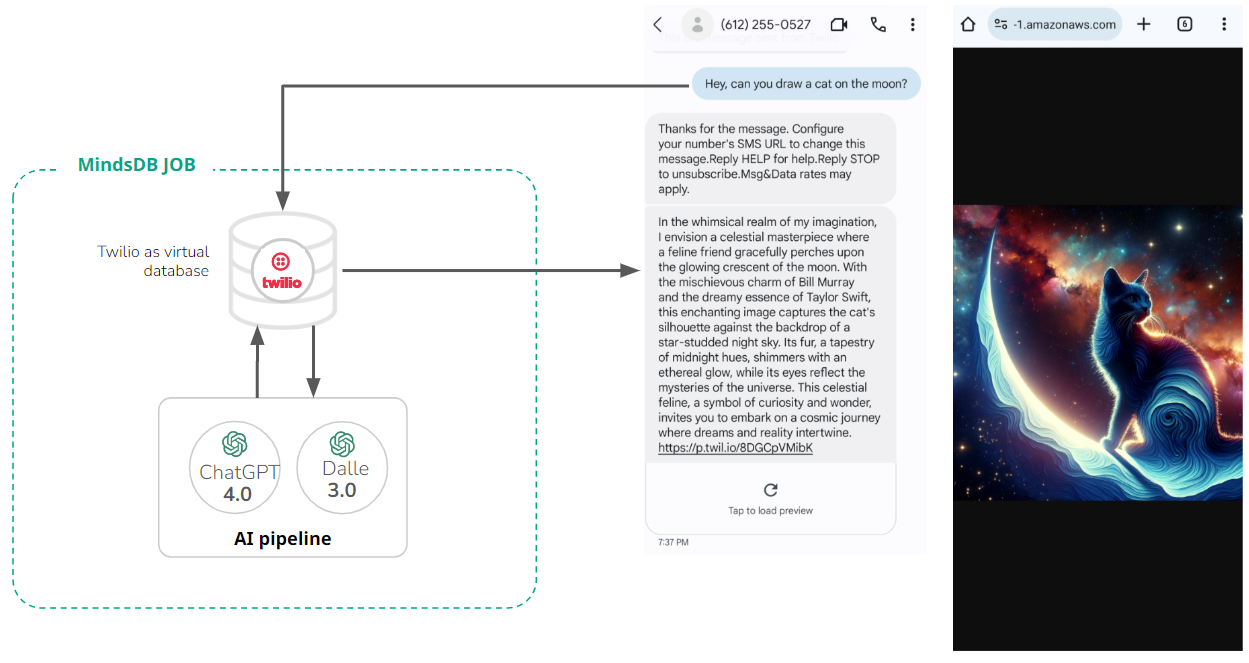
Step 2. Set up your Twilio account and connect it to MinsdDB
You can set up a Twilio account here, and then you get a virtual phone number in the console. This virtual number will be the one that sends a text to your personal number. Save the account string identifier (SID), auth token, and virtual phone number. Use this command to connect the Twilio account to MindsDB:Step 3. Automate the Twilio bot with MindsDB
We use the custom Jobs feature to schedule query execution.CREATE JOB statement. Within parenthesis, provide all statements to be executed by the job. Finally, schedule a job - here it’ll run once every two minutes.
This job inserts replies to Twilio messages into the messages table. We provide the SELECT statement as an argument to the INSERT statement. Note that the inner SELECT statement uses one model to generate a text response (aliased as outputtext). Then, the output is joined with another model that generates an image (aliased as outputimage) based on the text response generated by the first model.
You can monitor this job with the following commands: